Febantel vs Fenbendazole: A Comparative Analysis for Potential Cancer Treatments
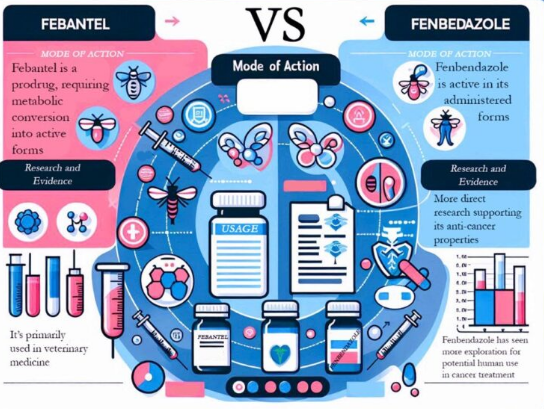
In the ongoing search for effective cancer treatments, unconventional medications are garnering attention. Febantel and Fenbendazole, both used traditionally as antiparasitic drugs, are among the potential candidates being studied. This article delves into their uses, efficacy, and potential as cancer treatments, providing a detailed comparison to enhance our understanding of these drugs. What Are Febantel and Fenbendazole? Febantel and Fenbendazole are both anthelmintic medications used to treat parasitic infections. They belong to the benzimidazole class of drugs, known for their ability to combat a wide range of parasites, including liver flukes. Febantel Febantel is primarily used in veterinary medicine to treat gastrointestinal parasites. It is a prodrug, meaning it is metabolized into its active form within the body, converting into fenbendazole and oxfendazole. This conversion enhances its anthelmintic efficacy against parasites such as liver flukes, roundworms, and tapeworms. Fenbendazole Fenbendazole is also an anthelmintic drug used mainly in veterinary contexts. It works by disrupting the energy metabolism of parasites, leading to their death. Like Febantel, it is effective against a range of parasites, including liver flukes and roundworms. Anthelmintic Efficacy and Cancer Recent research has explored the potential of both Febantel and Fenbendazole as anti-cancer agents. Their anthelmintic properties suggest they may also inhibit cancer cell growth and proliferation. Febantel’s Potential in Cancer Treatment While Febantel itself is less studied in cancer treatment, its metabolites, fenbendazole and oxfendazole, have shown promise. These metabolites are believed to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells and may interfere with their glucose metabolism. This dual action could potentially inhibit cancer cell growth and proliferation. Fenbendazole’s Anti-Cancer Properties Fenbendazole has garnered significant attention for its potential anti-cancer effects. Studies suggest that fenbendazole can disrupt microtubule formation in cancer cells, essential for their division and proliferation. Additionally, it may inhibit glucose uptake in cancer cells, starving them of energy and leading to their death. This dual mechanism of action makes fenbendazole a compelling candidate for further cancer research. Comparing Febantel and Fenbendazole While Febantel and Fenbendazole share similar properties and mechanisms, they have distinct differences: Safety and Side Effects Both Febantel and Fenbendazole are generally well-tolerated, but they come with potential side effects: Conclusion Febantel and Fenbendazole represent promising avenues in the exploration of non-traditional cancer treatments. While fenbendazole has more direct research and anecdotal support for its potential anti-cancer effects, Febantel’s metabolites, including fenbendazole itself, show significant promise. As research continues, these drugs may offer new hope for cancer patients seeking alternative therapies. However, it is crucial to consult healthcare professionals before considering any off-label use of these medications for cancer treatment. References Pantziarka, P., et al. (2014). Repurposing drugs in oncology (ReDO)—mebendazole as an anti-cancer agent. Ecancermedicalscience, 8, 443.
Febantel vs Fenbendazole: A Comparative Analysis for Potential Cancer Treatments Read More »